const int single pointer
In this section, you are going to learn
What is
const int a = 5;?What is
int const a = 5;?What is
const int *p = &a;?What is
int const *p = &a;?What is
int *const p = &a;?What is
const int *const p = &a;?
Inorder to answer above questions, let us remember a very simple rule
Anything after
constkeyword CAN NOT be changed
Is it that simple ?
Yes. Let us see how do we apply above rule to answer the questions
Step 1 : Consider the statement
const int a = 5;
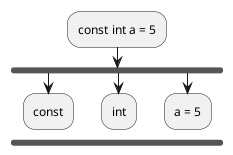
Step 2 : Remove all keywords after
const
const a = 5;
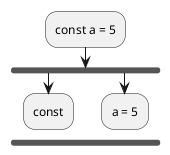
Step 3 : Remove everything before
const
const a = 5;
Step 4 : Remove assignment
const a;
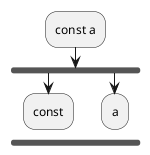
Step 5 : Now apply the rule. Anything after
constkeyword CAN NOT be changed
We see
aafterconstMeans, variable
aCAN NOT be changed again in next line
const int a = 5;
a = 10; // --> This is invalid
Step 1 : Consider the statement
const int *p = &a;
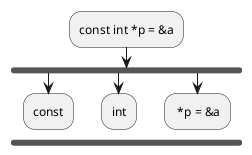
Step 2 : Remove all keywords after
const
const *p = &a;
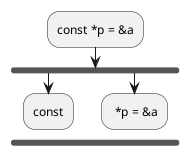
Step 3 : Remove everything before const
const *p = &a;
Step 4 : Remove assignment
const *p;
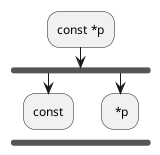
Step 5 : Now apply the rule. Anything after
constkeyword CAN NOT be changed
We see
*pafterconstMeans,
*pCAN NOT be changed again in next line
int a = 5;
const int *p = &a;
*p = 10; // --> This is invalid
Step 6 : Bonus point !
*pandpare different. Means you can changepFrom Step 4, we derived that “const *p”
Means only
*pis const and CAN NOT be changedBut remember
pis entirely differentThere is nothing which says
pis constantHence
pcan still be changedSee below example
int a = 5, b = 6;
const int *p = &a;
printf("*p is %d\n", *p); // prints 5
p = &b; // --> This is valid
printf("*p is %d\n", *p); // prints 6
Step 1 : Consider the statement
int *const p = &a;
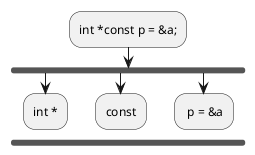
Step 2 : Remove all keywords after
const
int *const p = &a;
Step 3 : Remove everything before const
const p = &a;
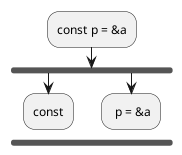
Step 4 : Remove assignment
const p;
Step 5 : Now apply the rule. Anything after
constkeyword CAN NOT be changed
We see
pafterconstMeans,
pCAN NOT be changed again in next line
int a = 5, b = 6;
int *const p = &a;
printf("*p is %d\n", *p); // prints 5
p = &b; // --> This is invalid
Step 6 : Bonus point !
*pandpare different. Means you can change*pFrom Step 4, we derived that “const p”
Means only
pis const and CAN NOT be changedBut remember
*pis entirely differentThere is nothing which says
*pis constantHence
*pcan still be changedSee below example
int a = 5, b = 6;
int *const p = &a;
printf("*p is %d\n", *p); // prints 5
*p = 100; // --> This is valid
printf("*p is %d\n", *p); // prints 100
There are two occurences of
constkeywordHence, let us apply the same rules two times
Step 1 : Consider the statement
const int *const p = &a;
Step 2 : Remove all keywords after first const
const *p = &a;
Step 3 : Remove everything before first const
const *p = &a;
Step 4 : Remove assignment
const *p;
Step 5 : Now apply the rule. Anything after const keyword CAN NOT be changed
*p CAN NOT be changed
Step 1 : Consider the statement
const int *const p = &a;
Step 2 : Remove all keywords after second const
const int *const p = &a;
Step 3 : Remove everything before second const
const p = &a;
Step 4 : Remove assignment
const p;
Step 5 : Now apply the rule. Anything after const keyword CAN NOT be changed
p CAN NOT be changed
Both p and *p CAN NOT be changed
int a = 5, b = 6;
const int *const p = &a;
*p = 100; // --> This is invalid
p = &b; // --> This is invalid
Statement |
Meaning |
|---|---|
const int a = 5; |
|
int const a = 5; |
|
const int *p = &a; |
|
int const *p = &a; |
|
int *const p = &a; |
|
const int *const p = &a; |
|
Current Module
Previous Module
Next Module
Other Modules